Heap¶
Binary heap properties¶
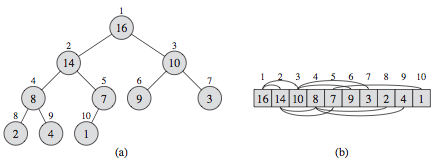
- Usually implemented using an array of elements but visualized as a complete binary tree (not a full binary tree).
- From the array index, we can compute the parent index from child's index and vice versa. The element values are partially ordered, briefly, they are ordered level by level. There is no ordering information of element values in the same level.
- The minimum number of elements in a binary heap with height h is 2^h, the maximum elements in it is 2^{h + 1} - 1
- The height of a binary heap is the floor of \log n. n is the total number of elements.
- The minimum element of a maximum heap is in the leaf nodes.
- With the array representation for storing an n-element heap, the leaves are the nodes indexed by \lfloor n/2 \rfloor + 1, \lfloor n/2 \rfloor + 2, \dots, n.
Heap sort¶
Heap implementation using an array¶
Heap implementation using HeapNode¶
Priority queue operations¶
Supported operations¶
| # | Operation | complexity | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | buildMaxHeap(A) | O(n) | Build a priority queue routine iteratively call maxHeapify() n/2 times. The complexity is O(n) instead of O(n \log n) |
| 2 | maxHeapify(A, i) | O(\log n) | Maintains the heap properties (by bubble up/down) for subtree rooted at i. Assumes the subtrees of i are max heap before calling this routine. |
| 3 | insert() | O(\log n) | Insert a element to the heap. |
| 4 | peekMaximum() | O(1) | Return the max element without remove it from the max-heap. |
| 5 | popMaximum() | O(\log n) | Remove the max element from the max-heap. |
| 6 | increaseKey() | O(\log n) | Update the element's key. This essentially changed the priority of an element. |
| 7 | delete() | Not supported by the binary heap implementation, but can be achieved by introduce more complex data structures. |
C++ STL priority queue¶
-
Notice if the elements in the queue is some complex container or object, you have to declare
priority_queuewith its underline container type, and the binary predicatestd::greaterif necessary. Here is an example in the solution of the problem Minimum Unique Word Abbreviationpriority_queue<pair<int, string>, vector<pair<int, string>>, greater<pair<int, string>>> pq; -
This line of code declared a priority queue
pq, whose element ispiar<int, string>, with the minimum element on the top. But minimum what? How the priority queue sort apair<int, string>element? In this case it implicitly sort thepair<int, string>element base on the first int value. How can we sort the priority queue element based on the second value of thepair<int, string>. To achieve that, we cannot use the building function object greater we have write a customized function object and pass to the declaration of thepqlike this,class mycomparison { public: mycomparison() {} bool operator() (const pair<int,string> &a, const pair<int,string> &b) const { return a.second.compare(b.second); } }; ... priority_queue<pair<int, string>, vector<pair<int, string>>, mycomparison> pq; ... -
We may need to write a customized binary predicate function in order to implement the
min-heapormax-heap. The binary predicate function depends on the underline container and also the type of the container element.
Java Priority Queue¶
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); // default is min heap
pq.add(1);
pq.add(2);
pq.poll(); // return the min value;
public class CustomerOrder implements Comparable<CustomerOrder> {
private int orderId;
private double orderAmount;
private String customerName;
public CustomerOrder(int orderId, double orderAmount, String customerName) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderAmount = orderAmount;
this.customerName = customerName;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CustomerOrder o) {
return o.orderId > this.orderId ? 1 : -1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "orderId:" + this.orderId + ", orderAmount:" + this.orderAmount + ", customerName:" + customerName;
}
public double getOrderAmount() {
return orderAmount;
}
}
Queue<CustomerOrder> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new CustomIntegerComparator());
// to overwrite the compareTo comparator
static class CustomerOrderComparator implements Comparator<CustomerOrder> {
@Override
public int compare(CustomerOrder o1, CustomerOrder o2)
{
return o1.getOrderAmount() < o2.getOrderAmount() ? 1 : -1;
}
}
Queue<CustomerOrder> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new CustomOrderComparator());
static class CustomIntegerComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 < o2 ? 1 : -1; // reverse ordering
}
}
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new CustomIntegerComparator());
Queue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
Python heapq package¶
Python heapq package provides a library of build heap data structure and heap related operations. It supports the following methods,
heapq.heappush(heap, item)heapq.heappop(heap)heapq.heappushpop(heap, item)heapq.heapify(list)heapreplace(heap, item)equivalent to heappoppush (not exists).heapq.merge(*iterable, key=None, reverse=False)heapq.nlargest(n, iterable, key=None)heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable, key=None)
Priority Queue¶
23 Merge k Sorted Lists¶
Solution 1 Priority queue
- Use a min priority queue to store all the list, iteratively pop the "min list", take the head node to the final list and push back to the priority queue if the "min list" still have node.
- Priority queue solution is O(N \log k)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class listComparison {
public:
listComparison() {}
bool operator(const ListNode* a, const ListNode* b) const {
return a->val > b->val;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, listComparison> q;
for (auto list : lists) {
if (list) {
q.push(list);
}
}
ListNode dummy(INT_MIN);
ListNode *curr = &dummy;
while (!q.empty()) {
curr->next = q.top(); q.pop();
curr = curr->next;
if (curr->next) {
q.push(curr->next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
Solution 2 Divide and conquer merge
- Use the divide and conquer idea to reduce the problem to a smaller problem and then solve the smallest problem, combined together with the solution of small problems, we will arrived at the final solution.
- Compare the following solution to merge sort algorithm.
- The complexity is O(N \log k) . Because merge two list will take O(N), and we will do O(\log k) time of merging.
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return mergeKListsHelper(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
ListNode* mergeKListsHelper(vector<ListNode*>& lists, int s, int e) {
if (s > e) return nullptr;
if (s == e) return lists[s];
if (s < e) {
int m = s + (e - s) / 2;
ListNode* l1 = mergeKListsHelper(lists, s, m);
ListNode* l2 = mergeKListsHelper(lists, m + 1, e);
return merge(l1, l2);
}
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummy(INT_MIN);
ListNode *curr = &dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
curr->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
curr->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
};
411 Minimum Unique Word Abbreviation¶
632 Smallest Range Covering Elements from K Lists¶
Solution 1 Priority queue
- Notice this solution pushed some meta data to the priority queue.
class Solution {
public:
struct mycompare {
bool operator () (pair<int, int>& a, pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.first > b.first;
}
};
vector<int> smallestRange(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, mycompare> pq;
int end = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
end = max(end, nums[i][0]);
// push the first element of kth vector and k to the pq
pq.push({nums[i][0], i});
}
vector<int> idx(n, 0); // keep tracking the index to the k arrays.
vector<int> res = {-100000, 100000}; // the range is given.
while (pq.size() == n) {
int start = pq.top().first;
int k = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (end - start < res[1] - res[0]) {
res[0] = start;
res[1] = end;
}
// if nums[k] have more element, we push next to the queue.
if (++idx[k] < nums[k].size()) {
pq.push({nums[k][idx[k]], k});
end = max(end, nums[k][idx[k]]);
}
}
return res;
}
};
215 Kth Largest Element in an Array¶
Solution 1 priority queue
- Build a heap takes
O(n). - max-heap
O(n) + O(klogk).
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int> pq(nums.begin(), nums.end());
k--;
while (k-- > 0) {
pq.pop();
}
return pq.top();
}
};
Solution 2 priority queue min-heap O(n*logk).
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
for (int n : nums) {
pq.push(n);
if (pq.size() > k) {
pq.pop();
}
}
return pq.top();
}
};
Solution 3 quickselect algorithm
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n < k) return 0;
return orderStats(nums, 0, n - 1, k);
}
int orderStats(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end, int k) {
if (start == end) return nums[start];
int p = partition(nums, start, end);
int order = p - start + 1;
if (order == k) {
return nums[p];
} else if (order > k) {
return orderStats(nums, start, p - 1, k);
} else {
return orderStats(nums, p + 1, end, k - order);
}
}
int partition(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) return 0;
int p = start + floor(rand() % (end - start + 1));
swap(nums[p], nums[end]);
int pivot = nums[end];
int i = start - 1, j;
for (j = start; j < end; ++j) {
if (nums[j] >= pivot) {
swap(nums[++i], nums[j]);
}
}
swap(nums[end], nums[i + 1]);
return i + 1;
}
};
218 The Skyline Problem¶
Solution 1 priority queue maximum heap
class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
int i = 0, x = 0, h = 0, len = buildings.size();
priority_queue<pair<int, int>> q; // max heap store <height, end>
while (i < len || !q.empty()) {
// building i start before the end of current tallest building
if (q.empty() || i < len && buildings[i][0] <= q.top().second) {
x = buildings[i][0]; // current start
// overlapped start of multiple buildings (compare to if)
while (i < len && buildings[i][0] == x) {
q.push({buildings[i][2], buildings[i][1]});
i++;
}
} else { // building i start after the end of current tallest building
x = q.top().second; // current end
// pop all buildings that end <= currently tallest buildings
while (!q.empty() && q.top().second <= x)
q.pop();
}
h = q.empty() ? 0 : q.top().first;
if (res.empty() || res.back().second != h) {
res.push_back({x, h});
}
}
return res;
}
};
Solution 2 multiset + scanline solution
class Solution {
private:
static bool cmp(pair<int,int> p1, pair<int,int> p2){
if(p1.first != p2.first) return p1.first < p2.first;
return p1.second > p2.second; // if x duplicate, tallest building first
}
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<pair<int, int>> h; // store the start and end.
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
multiset<int, greater<int>> s;
int prev = 0, curr = 0;
// scanline technique to obtain the starting point and end point
for (auto &a : buildings) {
h.push_back({a[0], a[2]});
h.push_back({a[1], -a[2]}); // use "-" mark the end point
}
sort(h.begin(), h.end(), cmp);
s.insert(0); // edge case, consider a.second == 0
for (auto &a : h) {
if (a.second > 0) s.insert(a.second); // if it is a start, insert to the set
else s.erase(s.find(-a.second)); // if it is a end, erase the inserted start
curr = *s.begin(); // take the maximum from the set
if (curr != prev) { // remove duplicate
res.push_back({a.first, curr});
prev = curr;
}
}
return res;
}
};
480 Sliding Window Median¶
Solution 1 heap + hash (simulated)
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> medianSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<double> res;
priority_queue<int> lo;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> hi;
unordered_map<int, int> hash_heap;
int i = 0;
while (i < k) lo.push(nums[i++]);
for (int j = 0; j < k / 2; j++) {
hi.push(lo.top());
lo.pop();
}
while (true) {
res.push_back(k & 1 ? lo.top() : ((double) lo.top() + (double) hi.top()) * 0.5);
if (i >= nums.size()) break;
int out_num = nums[i - k]; // first element in the window
int in_num = nums[i++]; // new element entering window
int balance = 0; // -1, when out_num in lo, +1 when out_num in hi.
// balance is the count of element diff in lo and hi.
// lo.size() == hi.size() -> balance = 0
// lo.size() > hi.size() --> balance > 0
// lo.size() < hi.size() --> balance < 0
balance += (out_num <= lo.top() ? -1 : 1);
hash_heap[out_num]++; // count of the invalid element, will remove when it on the top.
if (!lo.empty() && in_num <= lo.top()) {
balance++;
lo.push(in_num);
} else {
balance--;
hi.push(in_num);
}
if (balance < 0) { // lo lack of element.
lo.push(hi.top());
hi.pop();
balance++;
} else if (balance > 0) { // hi lack of element
hi.push(lo.top());
lo.pop();
balance--;
}
// lazy remove of elements previous removed, mimic hashheap of java.
while (!lo.empty() && hash_heap[lo.top()]) {
hash_heap[lo.top()]--;
lo.pop();
}
// lazy remove of elements previous removed, mimic hashheap of java.
while (!hi.empty() && hash_heap[hi.top()]) {
hash_heap[hi.top()]--;
hi.pop();
}
}
return res;
}
};
373. Find K Pairs with Smallest Sums¶
- use the following visual add when writing your code. The best solution choose the smallest K pairs layer by layer from top left to bottom right.
- From the visualization, you can see that this problem is equivalent to the problem Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix
2 4 6
+------------
1 | 3 5 7
7 | 9 11 13
11 | 13 15 17
def kSmallestPairs(self, nums1, nums2, k):
streams = map(lambda u: ([u+v, u, v] for v in nums2), nums1)
stream = heapq.merge(*streams) # streams is iterables
return [suv[1:] for suv in itertools.islice(stream, k)]
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/discuss/84551/simple-Java-O(KlogK)-solution-with-explanation
class cmp {
public:
bool operator() (const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.first + a.second < b.first + b.second;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> kSmallestPairs(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int k) {
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, cmp> pq;
for (int i = 0; i < min((int)nums1.size(), k); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < min((int)nums2.size(), k); ++j) {
pq.push({nums1[i], nums2[j]});
if (pq.size() > k) {
pq.pop();
}
}
}
while (!pq.empty()) {
res.push_back(pq.top()); pq.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> kSmallestPairs(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int k) {
// Base cases
if (nums1.size() == 0 || nums2.size() == 0 || k == 0) {
return { };
}
// Result pairs
vector<pair<int, int>> result;
// Prioritized scheduling based on sum (consider it as edge weight in graph)
// Similar to Prim's algorithm
// Min sum pq storing pair indices of nums1 index and nums2 index
auto pqCmp = [&nums1, &nums2](const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
return nums1[p1.first] + nums2[p1.second] > nums1[p2.first] + nums2[p2.second];
};
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(pqCmp)> pq(pqCmp);
// Visited is required to avoid duplicate scheduling
vector<vector<bool>> visited(nums1.size(), vector<bool>(nums2.size(), false));
// Push 0, 0 as the seed for scheduling
pq.push(make_pair(0, 0));
// Find k smallest sum pairs
while (k && !pq.empty()) {
// Current min sum index pair is at pq top
auto top = pq.top();
pq.pop();
result.push_back(make_pair(nums1[top.first], nums2[top.second]));
// Advance num1 index and schedule
++top.first;
if (top.first < nums1.size() && !visited[top.first][top.second]) {
pq.push(top);
visited[top.first][top.second] = true;
}
--top.first;
// Advance num2 index and schedule
++top.second;
if (top.second < nums2.size() && !visited[top.first][top.second]) {
pq.push(top);
visited[top.first][top.second] = true;
}
--top.second;
--k;
}
return result;
}
};
1046. Last Stone Weight¶
Solution 1 Using the heap property to keep tracking the top two stones and keep smashing them.
```python
class Solution:
def lastStoneWeight(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
pq = [-s for s in stones]
heapq.heapify(pq)
while len(pq) > 1:
heappush(pq, heappop(pq) - heappop(pq))
return -pq[0]
```
Use priority queue to rearrange tasks (characters, string, etc.)¶
358 Rearrange String k Distance Apart¶
Solution 1 Greedy + Priority Queue
class Solution {
public:
string rearrangeString(string s, int k) {
if (k <= 0) return s;
unordered_map<char, int> mp;
for (auto& c : s)
mp[c]++;
priority_queue<pair<int, char>, vector<pair<int, char>>, std::less<pair<int, char>>> pq; // max heap;
for (auto& p : mp) {
pq.push({p.second, p.first});
}
string res;
while (!pq.empty()) {
vector<pair<int, char>> used;
int i = 0;
while (i < k && !pq.empty()) {
auto t = pq.top(); pq.pop();
res.push_back(t.second);
i++;
if (--t.first > 0) {
used.push_back(t);
}
}
if (i != k && used.size())
return "";
for (auto& p : used) {
pq.push(p);
}
}
return res;
}
};
621 Task Scheduler¶
Solution 1 Greedy + Priority Queue
class Solution {
public:
class cmp {
public:
cmp () {}
bool operator()(const pair<int, char>& a, const pair<int, char>& b){
return a.first < b.first;
}
};
int leastInterval(vector<char>& tasks, int n) {
int chmap[26] = {0};
priority_queue<pair<int, char>, vector<pair<int, char>>, cmp> pq;
for (char c : tasks) {
chmap[c - 'A']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (chmap[i]) {
pq.push({chmap[i], i + 'A'});
}
}
int cycle = n + 1;
int res = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
vector<pair<int, char>> used;
for (int i = 0; i < cycle; ++i) { // pick total of n + 1 in freq order
if (!pq.empty()) {
used.push_back(pq.top()); pq.pop();
}
}
for (auto p : used) {
if (--p.first) {
pq.push(p); // put back used chars if extra char exist after the useage.
}
}
// handled partial cycle and full cycle
res += !pq.empty() ? cycle : used.size();
}
return res;
}
};
767 Reorganize String¶
Solution 1 Greedy + Priority Queue
class Solution {
public:
class cmp {
public:
cmp () {}
bool operator()(const pair<int, char>& a,const pair<int, char>& b){
return a.first < b.first;
}
};
string reorganizeString(string S) {
int n = S.length();
int chmap[26] = {0};
// max heap
priority_queue<pair<int, char>, vector<pair<int, char>>, cmp> pq;
for (auto& c : S) { //store to map
chmap[c - 'a']++;
}
// push to priority queue
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (chmap[i]) {
pq.push({chmap[i], i + 'a'});
}
}
if (pq.top().first > (n + 1) / 2) return "";
string res = "";
while (!pq.empty()) {
pair<int, char> p = pq.top(); pq.pop();
if (res.empty() || res.back() != p.second) {
res.push_back(p.second);
if (--p.first > 0) { // use one char
pq.push(p);
}
} else { // cannot use duplicate char, take another
pair<int, char> q = pq.top(); pq.pop();
res.push_back(q.second);
if (--q.first > 0) { // use another char
pq.push(q);
}
// remember put p back to the pq
pq.push(p);
}
}
return res;
}
};
1882. Process Tasks Using Servers¶
- Solution 1: Use two
PriorityQueues. Pay attention to the order criteria.
class Solution:
def assignTasks(self, servers: List[int], tasks: List[int]) -> List[int]:
readyQ, runningQ = [], []
res = []
for i in range(len(servers)):
heappush(readyQ, (servers[i], i))
for i, task in enumerate(tasks):
while runningQ and runningQ[0][0] <= i:
_, w, idx = heappop(runningQ)
heappush(readyQ, (w, idx))
if readyQ:
w, idx = heappop(readyQ)
else:
i, w, idx = heappop(runningQ)
res.append(idx)
heappush(runningQ, (i + task, w, idx))
return res
class Solution {
public int[] assignTasks(int[] servers, int[] tasks) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> readyQ = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> a[1] != b[1] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[2] - b[2]);
PriorityQueue<int[]> runningQ = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> (a[0] != b[0]) ? (a[0] - b[0]) :
((a[1] != b[1]) ? (a[1] - b[1]) : (a[2] - b[2])));
int m = servers.length;
int n = tasks.length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
// first element used for runningQ not readyQ
readyQ.add(new int[] {0, servers[i], i});
}
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!runningQ.isEmpty() && runningQ.peek()[0] <= i) {
readyQ.add(runningQ.poll());
}
if (readyQ.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = runningQ.poll();
res[i] = curr[2];
curr[0] += tasks[i];
runningQ.add(curr);
} else {
int[] curr = readyQ.poll();
res[i] = curr[2];
curr[0] = i + tasks[i];
runningQ.add(curr);
}
}
return res;
}
}